Tensorflow Direct Session (Draft)
摘要
本文主要分析了tensorflow 中DirectSession部分的代码。如果把executor 执行graph当成一个函数的话,那么Tensorflow中Session主要功能是把用户传过来的一些参数Feeds到compute graph中,然后运行到graph target node,最后在graph computation完成之后,取出用户指定名字的一些tensor。
DirectSession 则主要工作以下几方面:
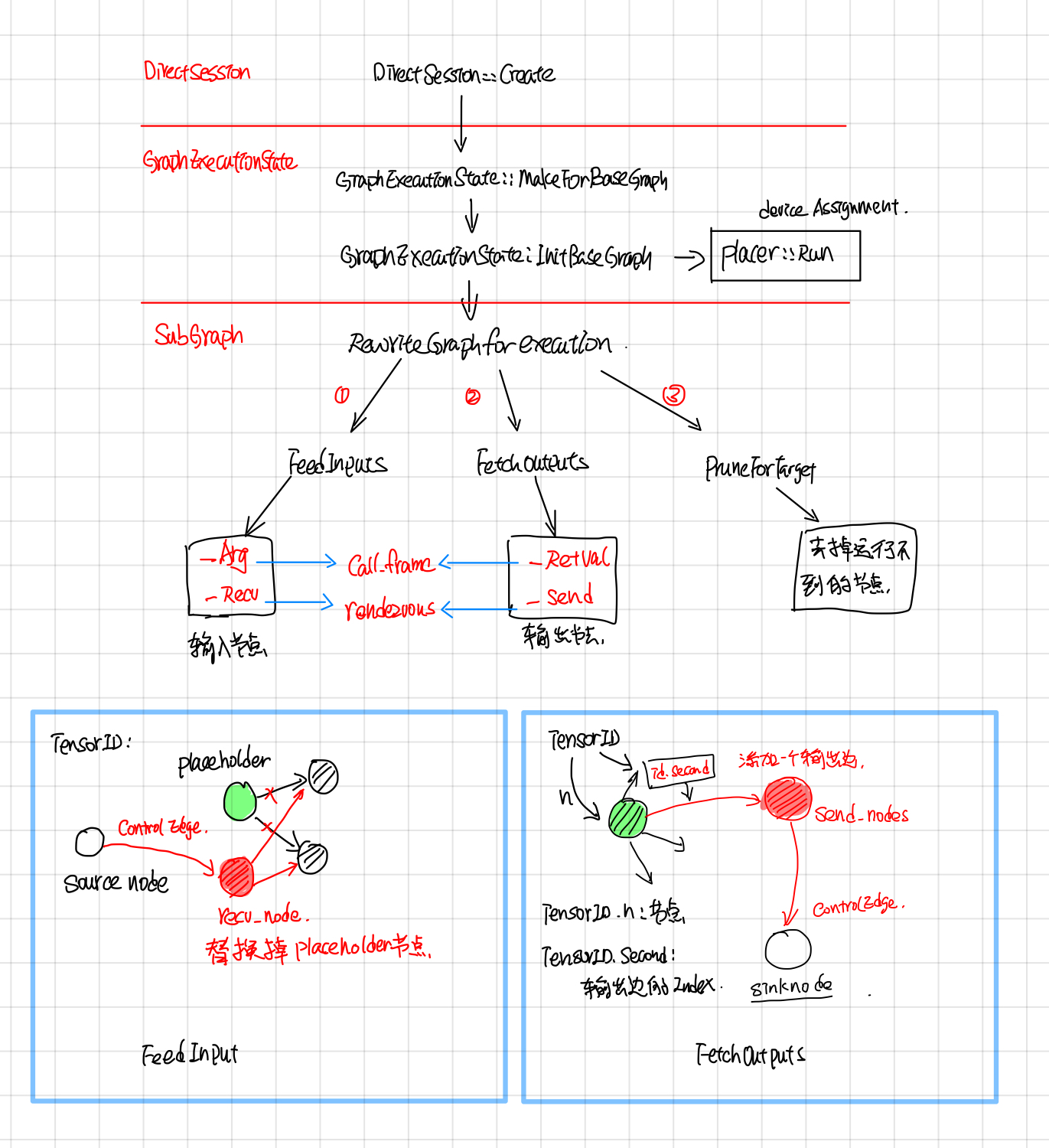
- Rewrite Graph: 将FeedInputs和FetchOutputs节点加到graph中,然后去掉graph中运行不到的节点,最后采用并查集的方式,给graph中每个node分配一个device。
- Graph partition:根据每个node所device,将node划分成不同的subgraph, subgraph之间添加send和recv节点做不同device之间的通信。
- CeateExecutors:每个device的subgraph会创建一个Executor来执行graph computation。
- Fetch outputs:对于DirectSession来说,FeedInputs和FetchOutputs 所添加的节点是
_Arg和_RetVal,这两个节点会通过directSession的callframe来读写input,output。
RewriteGraph
RewriteGraph这块的callstack如下图所示,主要主要涉及到 GraphExecutionState, SubGraph, Placer这三块。
GraphExecutionState据文档所说(graph_execution_state.h),其主要作用是按照BuildGraphOptions选项将Graph转换成可执行的Client Graph。
GraphExecutionState is responsible for generating an executable ClientGraph from the original GraphDef that specifies the complete graph and from BuildGraphOptions which specifies input/output nodes.
ClientGraph与GraphDef的区别是: ClientGraph中每个node都被Assign了某个Device,这部分由Placer完成;另外添加了input/output nodes, 去掉了执行不到的node, 这部分由subgraph完成。
An executable Graph differs from a GraphDef by being Placed, meaning that each Node is assigned to a single Device in the available set.
Call frame: feed and fetch
DirectSession中采用了call frame的方式读写compution graph中的inputs/outputs
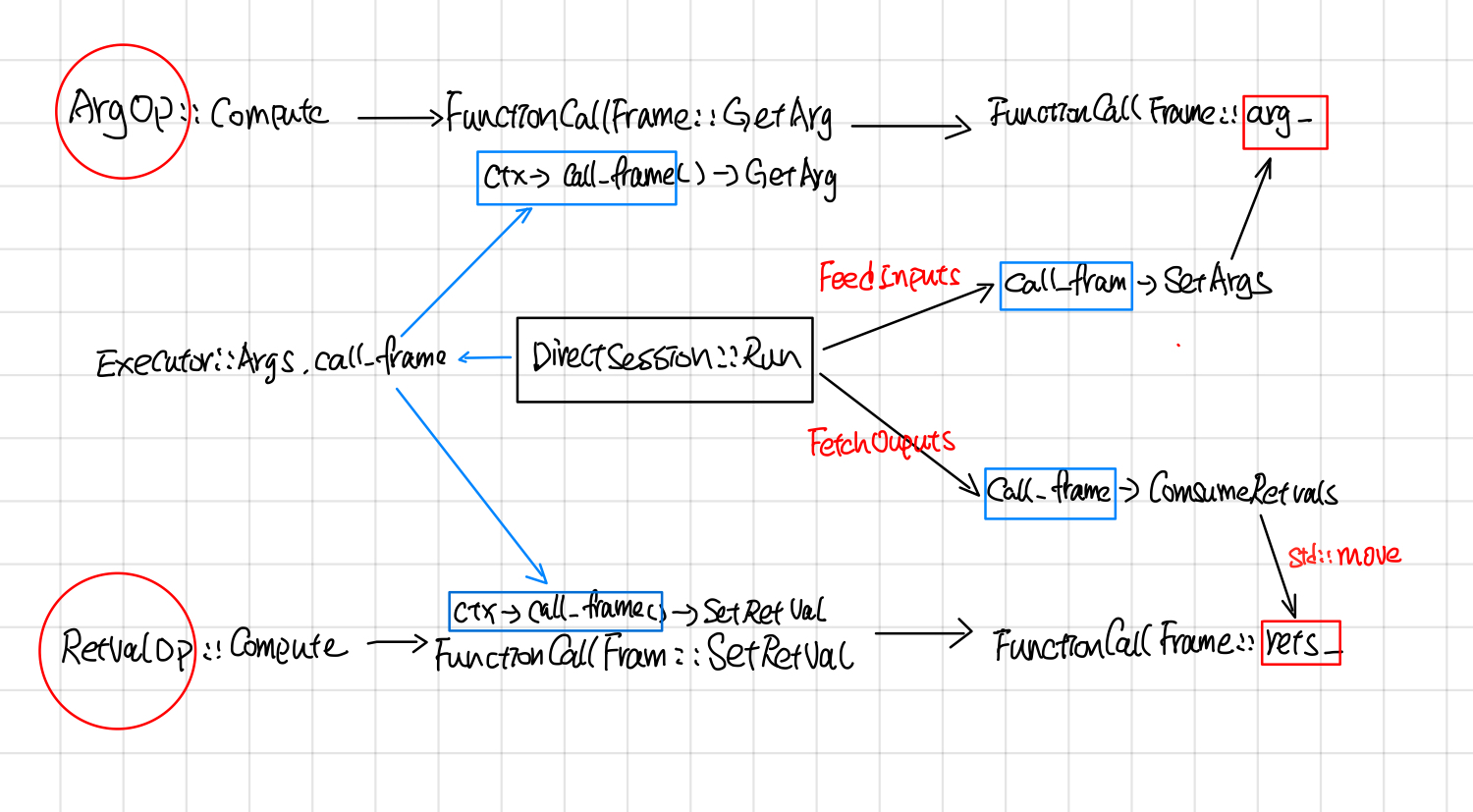
DirectSession::Run的时候,首先会创建一个FunctionCallFrame, 把要feed的tensor填充到FunctionCallFrame::args_。
// In DirectSession::Run
FunctionCallFrame call_frame(executors_and_keys->input_types,
executors_and_keys->output_types);
gtl::InlinedVector<Tensor, 4> feed_args(inputs.size());
for (const auto& it : inputs) {
if (it.second.dtype() == DT_RESOURCE) {
Tensor tensor_from_handle;
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(
ResourceHandleToInputTensor(it.second, &tensor_from_handle));
feed_args[executors_and_keys->input_name_to_index[it.first]] =
tensor_from_handle;
} else {
feed_args[executors_and_keys->input_name_to_index[it.first]] = it.second;
}
}
const Status s = call_frame.SetArgs(feed_args);
在创建Executor的时候,通过Executor::Args.call_frame把call_frame放到OpkernalContext中。
//## DirectSessioin::Runinternal
Executor::Args args;
args.step_id = step_id;
args.call_frame = call_frame;
//other code...
//每个device subgraph对应一个item, item.executor为这个subgraph的exeuctor.
item.executor->RunAsync(args, barrier->Get());
//## ExecutorState::Process
OpKernelContext::Params params;
params.step_id = step_id_;
params.call_frame = call_frame_;
//other code ...
// Synchronous computes.
OpKernelContext ctx(¶ms, item.num_outputs);
nodestats::SetOpStart(stats);
device->Compute(CHECK_NOTNULL(op_kernel), &ctx);
当所有的subgraph Executor执行完毕后,通过FunctionCallFrame::ConsumeRetVals的方式把输出的tensor取出来。
// DirectSession::Run
if (outputs) {
std::vector<Tensor> sorted_outputs;
const Status s = call_frame.ConsumeRetvals(&sorted_outputs);
if (errors::IsInternal(s)) {
//other code
Device placer
Placer 在初始的时候,用户会指定某些节点的device, 比如有的节点是gpu:0, 有的cpu:0, 有的node是gpu:1, 然后将有相同class_属性@loc:xxx的node节点放到一个集合里面,随后根据以下约束, 采用并查集的方式,对node集合进行进一步的划分:
- 用户指定了device,就将node放到用户指定的device上
- Generateo node 和output node放到同一个device上
- Meta node(比如cast操作) 和input node放到同一个device上
- Reftype 的Input, input和output节点尽量放到同一个device上
- 采用并查集的方式将node place给device
- 对于stateful的node, 不改变它的device assign。
stateful node 在placed之后,就不能移到别的device上了, 对于这种node,GraphExecutionState的做法是在placer run之前将stateful node的device assign保存以下,在placer run 之后再恢复回去。
Map of placed stateful nodes, i.e. nodes for which is_stateful() is true, such as "params" and "queue" nodes. Once placed these nodes can not be moved to a different device. Maps node names to device names.
可以通过打开log_device_placement的方式让placer在stderr中把node的device place情况打出来:
config=tf.ConfigProto(log_device_placement=True)
sess = tf.Session(config=config)
Graph partition
Graph partition根据上面Placemnet的结果,将graph partition成不同的子图,子图之间添加send 和recv节点,send和recv节点会用rendzvous来传送tensor。有时候除了send和recv node还需要添加一些control flow node。
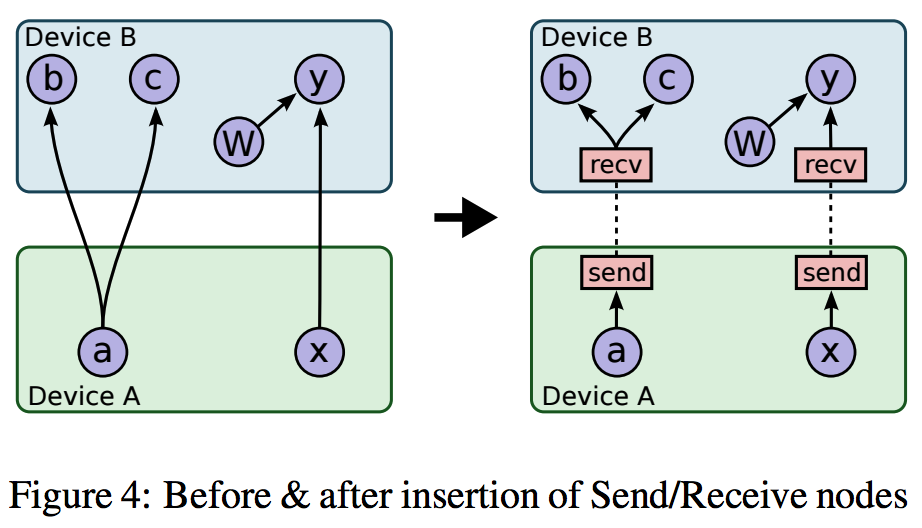
(这个地方需要看下tf implement那个文档,了解下具体情况)
Executor Cache
提交给DirectSessoin在经过Graph Partition之后,会划分成不同的子图,比如下图将一个大的graph划分成了3个subgraph分别放置在了在CPU, GPU1, GPU2上,device之间通过rendezvous来通信,每个subgraph都会创建一个executor去执行。
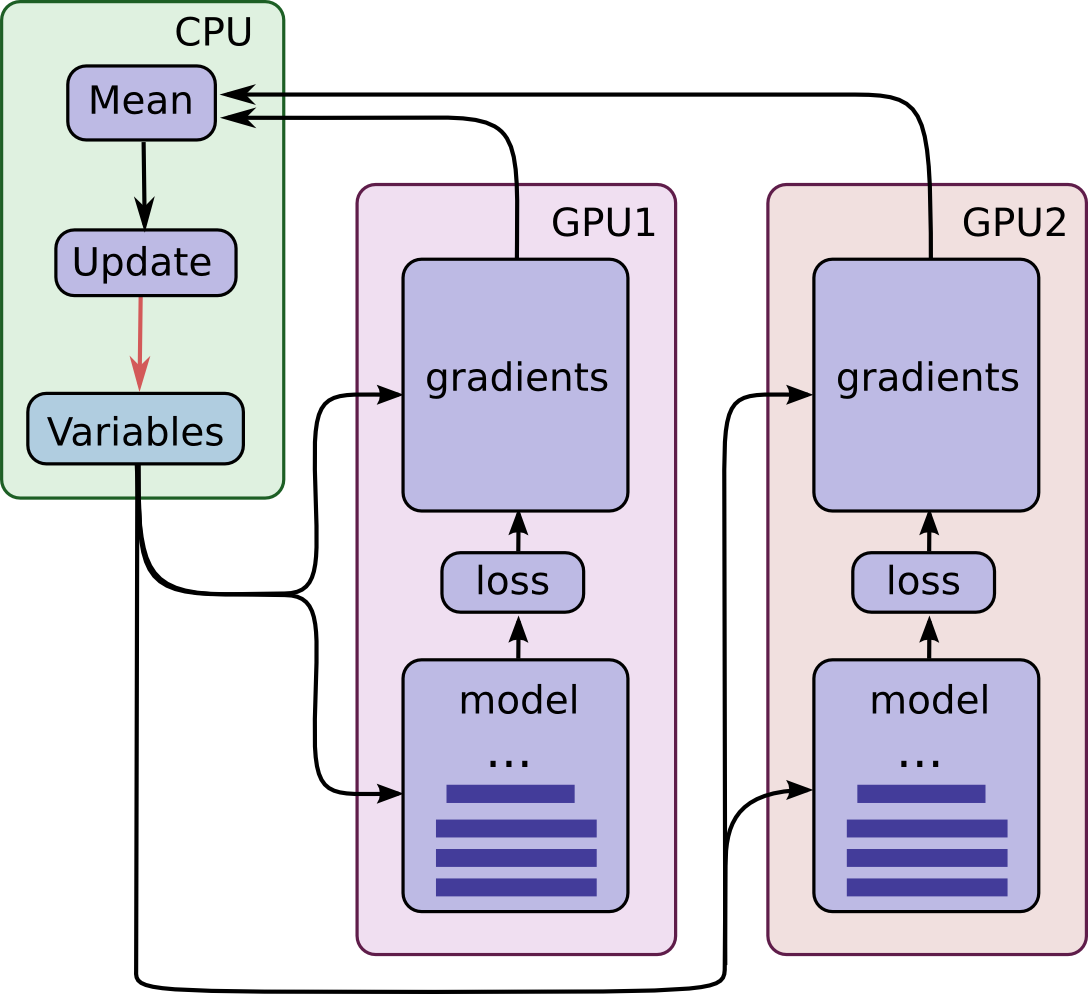
在模型的训练通常会多次迭代run, 因此要加一层cache避免多次做graph的parition,多次创建executor。
with tf.Session(config=config) as sess:
sess.run([merge, gd_step], feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y_label: batch_ys})
cache的key为input, output,target tensor的names 连起来的。还有一个key是吧input, output, target的names分别sort之后再连起来。
DirectSession::Run中cache的key很有意思,有两个key, 首先去是未排序的,另外一个是排序的。未排序的为了快速查找,而排序的key是为了避免由于input_names中names顺序不一样导致cache miss。
// Fast lookup path, no sorting.
// Fast查询的key, 没排序
const string key = strings::StrCat(
str_util::Join(inputs, ","), "->", str_util::Join(outputs, ","), "/",
str_util::Join(target_nodes, ","), "/", run_state_args->is_partial_run,
"/", debug_tensor_watches_summary);
// 将names分别排序然后concat起来.
std::vector<string> inputs_sorted(inputs.begin(), inputs.end());
std::sort(inputs_sorted.begin(), inputs_sorted.end());
std::vector<string> outputs_sorted(outputs.begin(), outputs.end());
std::sort(outputs_sorted.begin(), outputs_sorted.end());
std::vector<string> tn_sorted(target_nodes.begin(), target_nodes.end());
std::sort(tn_sorted.begin(), tn_sorted.end());
const string sorted_key = strings::StrCat(
str_util::Join(inputs_sorted, ","), "->",
str_util::Join(outputs_sorted, ","), "/", str_util::Join(tn_sorted, ","),
"/", run_state_args->is_partial_run, "/", debug_tensor_watches_summary);
// Set the handle, if its needed to log memory or for partial run.