RawNode
raft module
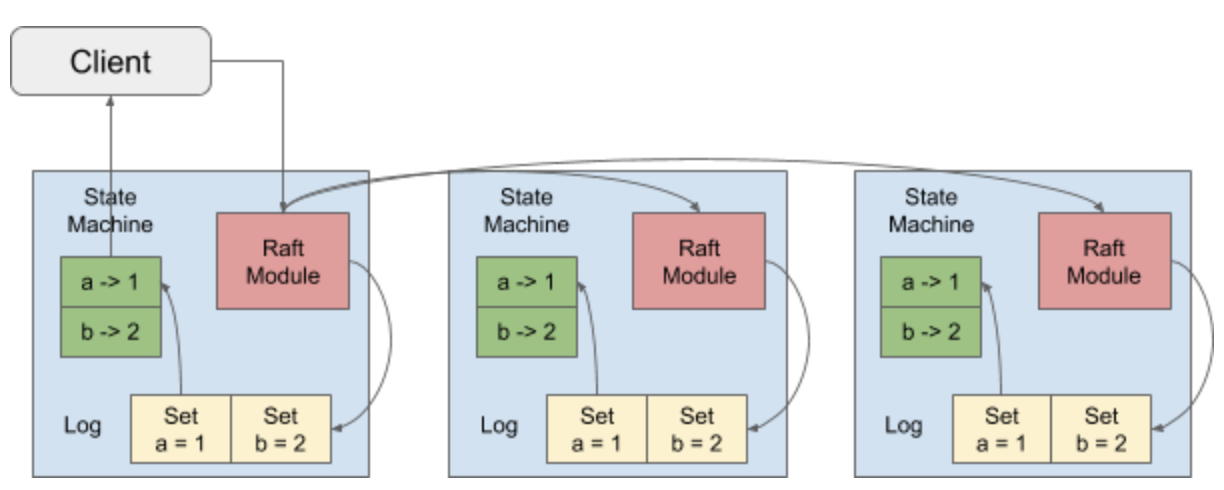
基本过程为,client发读写请求给raft leader。
raft leader在处理写请求(比如put k, v)时,将写请求包装为一个log entry, 写到自己 本地的raft log中,然后发给各个follower, follower写成功后,发送ack给leader, 当集群中 大部分节点写成功时(达到commit状态,可以安全的apply 到state machine上,leader返回写成功给client.
leader在处理读请求时,会通过read index检查确认自己还是不是leader,
RawNode API
raft对外暴露的接口为RawNode,它和App关系如下图所示:
App在处理client write操作时候,调用Raft Propose 将writes数据作为log entry写入 到raft log。 等该log entry在raft group中达到commit状态时,Client write操作就可以返回了。
App通过RawNode的tick 来驱动raft的logical时钟(驱动leader节点发送hearbeat, follower节点累计触发election timeout)
调用RawNode::step将其他节点发来的raft message发给raft处理。
然后调用RawNode Ready获取需要发送给raft peer的Message, 需要持久化保存的log entries, 以及需要apply 到state machine的log entries.
最后App调用RawNode的advance,Raft更新完一些状态后,准备处理App下一次调用。
tick
RawNode::tick 定时时钟,用来驱动leader的定期的向follower/candidate 发送
heartbeat, 而follower则在累积election timoout, 如果follower如果发现超过election timeout没收到
leader的心跳包,则会成为candidate发起campaign.
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { /// Tick advances the internal logical clock by a single tick. /// /// Returns true to indicate that there will probably be some readiness which /// needs to be handled. pub fn tick(&mut self) -> bool }
step
App会调用RawNode::step来处理集群其他peer发来的Message。
比如Leader的heartbeat, leader的AppendMsg, candidate的vote request, follower节点的heartbeat resp, append resp, vote resp等消息。
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { /// Step advances the state machine using the given message. pub fn step(&mut self, m: Message) -> Result<()> }
propose
App 通过RawNode::propose来write data到raft log,当这个log entry被
复制到集群大部分节点,并且可以被安全提交时候,App调用 RawNode::ready
获取可以被安全的applied到state machine上的log entries,
把它们apply到state machine上。
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { /// Propose proposes data be appended to the raft log. pub fn propose(&mut self, context: Vec<u8>, data: Vec<u8>) -> Result<()> }
propose_conf_change
App调用RawNode::propose_conf_change来提交对raft 集群成员的配置修改,
等该提交committed, 并且App把集群配置信息保存好后,
App调用RawNode::apply_conf_change 真正的去修改
Raft的集群配置(对应于Raft的ProgressTracker)
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { /// ProposeConfChange proposes a config change. /// /// If the node enters joint state with `auto_leave` set to true, it's /// caller's responsibility to propose an empty conf change again to force /// leaving joint state. #[cfg_attr(feature = "cargo-clippy", allow(clippy::needless_pass_by_value))] pub fn propose_conf_change(&mut self, context: Vec<u8>, cc: impl ConfChangeI) -> Result<()> { }
read_index
App调用RawNode::read_index 来获取read_index
除此之外raft中还有一个lease read.
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { /// ReadIndex requests a read state. The read state will be set in ready. /// Read State has a read index. Once the application advances further than the read /// index, any linearizable read requests issued before the read request can be /// processed safely. The read state will have the same rctx attached. pub fn read_index(&mut self, rctx: Vec<u8>) { }
从step 到Ready
App先将hardstate, log entries等保存下来,再将raft message 发出去。
Raft::msgs
发送的消息都会暂存在Raft::msgs数组中,在RawNode::ready被调用时, 会先放到RawNode::records中,等entries都保存完后, app再取到这些消息,将消息发送给对应的peers.
leader
leader会主动定期的发送Heartbeat给follower。 在处理follower的heartbeat resp和Append resp中 会发送AppendEntry(MsgSnapshot, MsgAppend)消息给follower
follower
follower 处理leader发送的heartbeat消息和Append消息,然后 发送HeartBeatResp和AppendResp给leader
candidate
如果在投票期间收到了其他leader的消息,并且验证(term不小于自己的term)Ok的话, 就成为follower,处理heartbeat, appendEntry等消息,流程和上面的follwer一样。
如果没有其他leader的消息,就处理peer发来的投票resp,
如果只是赢得了PRE_ELECTION 就接着发起ELECTION,如果赢了ELECTION,就成为新的leader,
然后立刻bcast_append 发送消息所有peers.
entries
snapshot
hardState and softState
hardstate:
- term:当前任期,
- vote: 给谁投票了。
- commit: 当前的commit index
softstate 则包含leaderId是谁,当前node的角色是什么

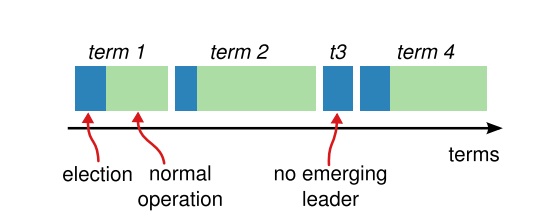
term 扮演逻辑时钟的角色.
read states
在处理读请求时,从Leader节点读数据,leader节点需要确认自己是否还是leader ,如果从follower节点读数据,follower节点要知道当前leader节点的committed index, 等自己的state machine apply到这个committed index后,再回复数据给client.
Raft提供了两种方法一个是ReadIndex,ReadIndex就是leader节点广播一次心跳,确认自己是leader.
另外一种是LeaseRead, 他假设leader 的 lease 有效期可以到 start + election timeout / clock drift bound 这个时间点。需要各个服务器之间的clock频率是准的,在lease有效期内,不用发送心跳。
ReadState 负责记录每个客户端读请求状态,
request_ctx: 客户端唯一标识index: committed index
ready
RaftCore::step之后,raft会产生一系列的状态更新,比如要发送raft message, 有些committed log entry 需要apply到state machine上, 有些log entry 需要保存等.
App通过调用RawNode::ready 返回的struct Ready来获取这些更新
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { /// Returns the outstanding work that the application needs to handle. /// /// This includes appending and applying entries or a snapshot, updating the HardState, /// and sending messages. The returned `Ready` *MUST* be handled and subsequently /// passed back via advance() or its families. /// /// `has_ready` should be called first to check if it's necessary to handle the ready. pub fn ready(&mut self) -> Ready }
Ready struct如下:
其中主要字段如下:
hs: Raft 相关的元信息更新,如当前的term,投票结果,committed index 等等。LightReady::committed_entries: 最新被 commit 的日志,需要apply到state machine上。LightReady::messages: 需要发送给其他 peer的Message。Ready::snapshot: 需要apply到state machine 的snapshot。Ready::entries: 需要保存的 log entries。Ready::ReadState:read_index?
解释下ReadyRecord, max_number, records的作用。
需要注意的是,Raft需要把entries持久化,才能把message发出去。 所以这个地方用了ReadyRecord先把message 保存起来, 等RawNode::advance之后,才会把message放到RawNode::messages数组。
advance
应用在保存完ready中的entries, apply完snapshot, 发送完messages之后, 调用RawNode::advance更新raft一些状态。
主要会更新
RaftLog::persisted: 表示已经持久化保存日志的indexRaftLog::committed_index: 由ProgressTracker的votes来计算committed indexRaftLog::applied: 已经apply 到state machine的index