2pc
数据流程
TiDB中乐观事务提交流程如下(摘自TiDB 新特性漫谈:悲观事务)
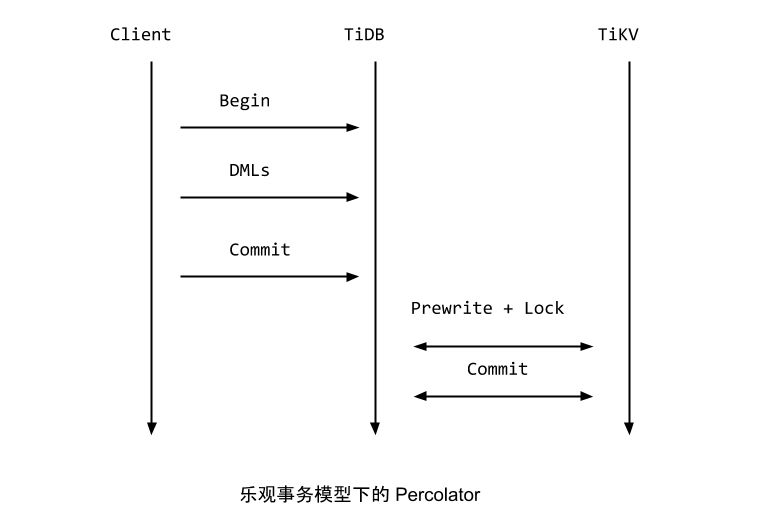
- 首先Begin 操作会去TSO服务获取一个timestamp,作为事务的
startTS,同时startTs也是事务的唯一标识。 - DML阶段先KVTxn将写(Set, Delete)操作保存在
MemDB中。 - 2PC提交阶段在
KVTxn::Commit时创建twoPhaseCommitter, 并调用它的initKeysAndMutations遍历MemDB, 初始化memBufferMutations. - 在
twoPhaseCommitter::execute中,首先对memBufferMutations先按照region做分组,然后每个分组内,按照size limit分批。 - 每批mutations,调用对应的action的
handleSignleBatch,发送相应命令到TiKV.
Begin Transaction
每个client connection 对应着一个session, 事务相关数据的放在了session中, 它包含了对kv.Storage和Txn接口的引用。
kv.Storage接口定义了Begin/BeginWithOption接口,用来创建开始一个事务,它
主要实现者为KVStore。
kv.Transaction定义了事务的接口,txn可以commit/rollback.
它主要实现者为KVTxn。
每个KVTxn有个对MemDB的引用,每个事务的set/delete等修改会先存放到MemDB中。
kv.Storage的Begin/BeginWithOption 调用图如下:如果startTS为nil, 则会去TOS(timestamp oracle service)也就是 PD服务获取一个时间戳,作为事务的startTS,同时也是事务的唯一标识。
数据DML: 先保存到txn的MemDB
table row的增删改,最终会调用Table的AddRecord, RemoveRecord, UpdateRecord接口来更新数据。
而Table的这些接口,会将改动保存在Txn.KVUnionStore.MemDB中。
twoPhaseCommitter
像pecolator论文中描述的协议一样,两阶段提交步骤如下:
- 先Prewrite获取Lock, TiDB中可以并发的发起Prewrite请求.
- 去TSO 服务获取commit ts, 保证获取的
commit_ts比之前的事务的start_ts都大。 - commit primary key, 提交完primary key后,就可以返回给client,事务提交成功了。
- 其它剩下的keys由go routine在后台异步提交。
下图摘自[Async Commit 原理介绍][async-commit]
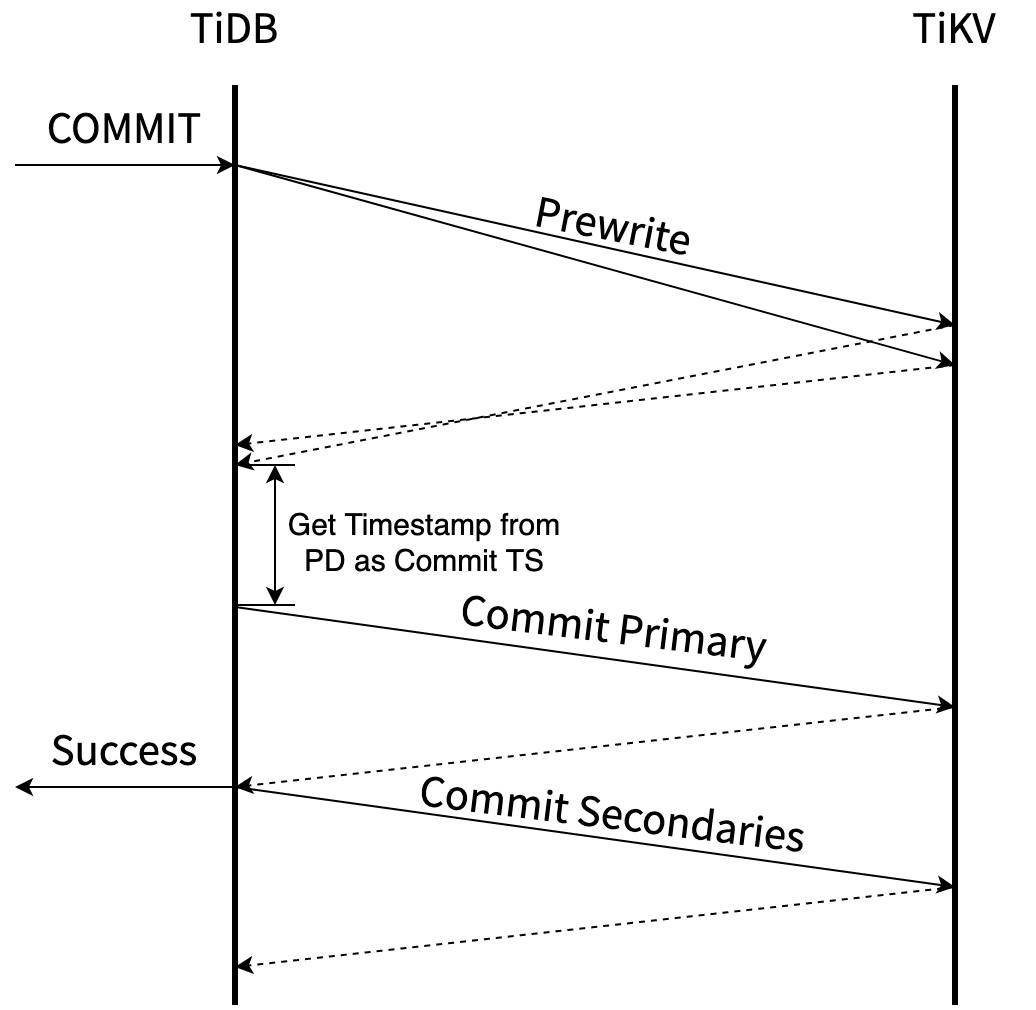
TiDB中会先根据region对MemDB中的keys做分组,然后每个分组内做分批,最后一批一批的向TiKV发请求。
mutations
上面保存在txn的MemDB中的修改,在txn commit时,会被转变为twoPhaseCommitter::mutations,在两阶段提交的
Prewrite/Commit阶段会提交这些mutations.
doActionOnMutations
// doActionOnMutations groups keys into primary batch and secondary batches, if primary batch exists in the key,
// it does action on primary batch first, then on secondary batches. If action is commit, secondary batches
// is done in background goroutine.
先调用groupMutations, 将mutations按照region分组,然后doActionOnGroupMutations对每个group分别做处理。
groupMutations: 按照region分组
先对mutations按照region分组,如果某个region的mutations 太多。 则会先发送CmdSplitRegion命令给TiKV, TiKV对那个region先做个split, 然后再开始提交, 这样避免对单个region too much write workload, 避免了不必要的重试。
doActionOnGroupMutations: 分批
doActionOnGroupMutations 会对每个group的mutations 做进一步的分批处理。 对于actionCommit做了特殊处理,如果是NormalCommit, primay Batch要先提交, 然后其他的batch可以新起一个go routine在后台异步提交。
关键代码如下:
func (c *twoPhaseCommitter) doActionOnGroupMutations(bo *Backoffer, action twoPhaseCommitAction, groups []groupedMutations) error {
// 1.每个分组内的再分批
for _, group := range groups {
batchBuilder.appendBatchMutationsBySize(group.region, group.mutations, sizeFunc, txnCommitBatchSize)
}
//2.commit先同步的提交primary key所在的batch
if firstIsPrimary &&
((actionIsCommit && !c.isAsyncCommit()) || actionIsCleanup || actionIsPessimiticLock) {
// primary should be committed(not async commit)/cleanup/pessimistically locked first
err = c.doActionOnBatches(bo, action, batchBuilder.primaryBatch())
//...
batchBuilder.forgetPrimary()
}
//...
//3. 其它的key由go routine后台异步的提交
// Already spawned a goroutine for async commit transaction.
if actionIsCommit && !actionCommit.retry && !c.isAsyncCommit() {
//..
go func() {
//其它的action异步提交
e := c.doActionOnBatches(secondaryBo, action, batchBuilder.allBatches())
}
}else {
err = c.doActionOnBatches(bo, action, batchBuilder.allBatches())
}
//...
doActionOnBatches: 并发的处理batches
batchExecutor::process 每个batch会启动一个go routine来并发的处理,
并通过channel等待batch的处理结果。当所有batch处理完了,再返回给调用者。
其中会使用令牌做并发控制, 启动goroutine前先去获取token, goroutine运行 完毕,归还token。
actionPrewrite
发送prewrite命令到TiKV, 如果prewrite阶段,遇到了lock error, 则尝试Resole lock, 然后重试;如果遇到了regionError, 则需要重新 调用doActionONMutations,重新分组,重新尝试。
如果没有keyError,并且Batch是primary. 则启动一个tllManager,给txn的 primary lock续命,ttlManager会定期的向TiKV发送txnHeartbeat, 更新primary lock的ttl。
TiKV端处理Prewrite
TiKV端PreWriteKind,分为悲观事务和乐观事务。
对单个key Muation的prewrite操作。
constraint check
should not write
PrewriteMutation
TiKV端处理TxnHeartBeat
直接更新primary key lock的ttl.
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { //txn_heart_beat.rs impl<S: Snapshot, L: LockManager> WriteCommand<S, L> for TxnHeartBeat { fn process_write(self, snapshot: S, context: WriteContext<'_, L>) -> Result<WriteResult> { //... let lock = match reader.load_lock(&self.primary_key)? { Some(mut lock) if lock.ts == self.start_ts => { if lock.ttl < self.advise_ttl { lock.ttl = self.advise_ttl; txn.put_lock(self.primary_key.clone(), &lock); } lock } }
actionCommit
TiDB向Tikv发起commit请求,CommitRequest中的Keys即为要提交的key.
TiKV端处理commit
TiKV会遍历Commit请求中的每个key, 尝试去commit key, 然后调用ReleasedLocks唤醒等待这些key的事务。
单个key的commit过程如下, 分两种case:
lock match: lock仍然被txn 所持有,则继续尝试提交, 提交如果commit_ts < lock.min_commit_ts则报错,ErrorInner::CommitTsExpired,如果lock.rollback_ts中有和commit_ts相同的ts, 则需要将 要写入的write.set_overlapped_rollback。最后unlock key, 提交write。lock mismatch: lock为None或者Lock已经被其他事务所持有,则需要get_txn_commit_record读取commit record来判断事务的commit状态.
参考文献
Draft
事务startTS
在执行start transaction时,会去TimmStamp Oracle服务获取时间戳,作为事务的startTS, startTs会保存在TransactionContext中 startTS 是单调递增的,这样startT标识事务, 也可以用来表示事务之间的先后关系。
在TiDB中,对应流程如下: