AsyncCommit
AsyncCommit 等所有的key prewrite之后,就算成功了,TiDB即可返回告诉client事务提交成功了。 primary key 可以异步的commit.其流程如下(摘自Async Commit 原理介绍)
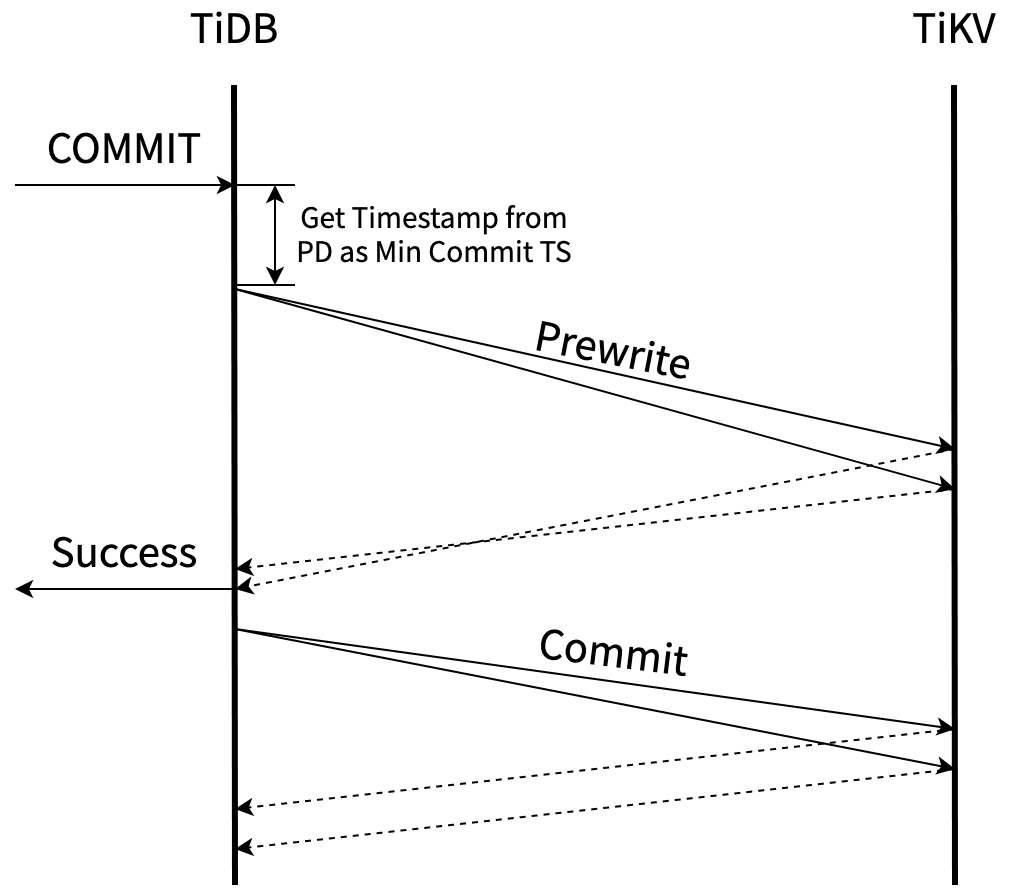
好处是在prewrite结束后,就可以返回结果给client, commit由tidb在后台异步提交,降低了事务的延迟。
需要解决的主要有两个:
- 从如何确定所有 keys 已被prewrite,需要根据primary key找到所有的secondary keys.
- 如果确定
commit_ts
对于问题1,primarylock中增加了pub secondaries: Vec<Vec<u8>>字段。
lock 包含了txn涉及到的所有的 secondaries keys
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { #[derive(PartialEq, Clone)] pub struct Lock { pub lock_type: LockType, pub primary: Vec<u8>, pub ts: TimeStamp, pub ttl: u64, pub short_value: Option<Value>, // If for_update_ts != 0, this lock belongs to a pessimistic transaction pub for_update_ts: TimeStamp, pub txn_size: u64, pub min_commit_ts: TimeStamp, pub use_async_commit: bool, // Only valid when `use_async_commit` is true, and the lock is primary. Do not set // `secondaries` for secondaries. pub secondaries: Vec<Vec<u8>>, // In some rare cases, a protected rollback may happen when there's already another // transaction's lock on the key. In this case, if the other transaction uses calculated // timestamp as commit_ts, the protected rollback record may be overwritten. Checking Write CF // while committing is relatively expensive. So the solution is putting the ts of the rollback // to the lock. pub rollback_ts: Vec<TimeStamp>, } }
问题2,则使用每个key的min_commit_ts和TiKV的max_ts来确定事务的commit_ts TiDB的每次读都会更新Tikv的max_ts。
对于 Async Commit 事务的每一个 key,prewrite 时会计算并在 TiKV 记录这个 key 的 Min Commit TS,事务所有 keys 的 Min Commit TS 的最大值即为这个事务的 Commit TS。
checkAsyncCommit
先关配置在Config.TiKVClient.AsyncCommit中, checkAsyncCommit 会遍历mutations
计算事务的total key size是否超过了限制。 最后结果保存在atomic变量useAsyncCommit中。
相关配置项如下:
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { type AsyncCommit struct { // Use async commit only if the number of keys does not exceed KeysLimit. KeysLimit uint `toml:"keys-limit" json:"keys-limit"` // Use async commit only if the total size of keys does not exceed TotalKeySizeLimit. TotalKeySizeLimit uint64 `toml:"total-key-size-limit" json:"total-key-size-limit"` // The duration within which is safe for async commit or 1PC to commit with an old schema. // The following two fields should NOT be modified in most cases. If both async commit // and 1PC are disabled in the whole cluster, they can be set to zero to avoid waiting in DDLs. SafeWindow time.Duration `toml:"safe-window" json:"safe-window"` // The duration in addition to SafeWindow to make DDL safe. AllowedClockDrift time.Duration `toml:"allowed-clock-drift" json:"allowed-clock-drift"` } }
isAsyncCommit caller
对isAsyncCommit的调用, 最主要的有两个地方
- prewrite阶段,是buildPrewriteRequest时,需要遍历事务的 mutations将所有的secondaries lock keys 放到request中
- commit阶段,commit时,启动一个go routine 异步提交,这样prewrite成功后,就可以向client返回事务结果, 不必向正常commit时等到primary key,提交成功才返回结果给client.
minCommitTS
对于 Async Commit 事务的每一个 key,prewrite 时会计算并在 TiKV 记录这个 key 的 Min Commit TS,事务所有 keys 的 Min Commit TS 的最大值即为这个事务的 Commit TS。
client端更新min commit ts
minCommitTS更新逻辑如下,twoPhaseCommitter有个成员变量minCommitTS,记录事务的最小CommitTS.
每次prewrite request会带上该minCommitTS, 并且如果prewrite resp返回的minCommitTS比自己的大,
则更新twoPhaseCommitter的minCOmmitTS
这样能保证所有prewrite 请求处理完后,twoPhaseCommitter的minCommitTS是所有key lock的minCommitTS
中最大的。
在后面resolve async commit lock中,也要遍历所有的lock的minCommitTS, 来确定最后的minCommitTS.
- PreWrite前从TSO获取ts, 更新成员变量
minCommitTS
func (c *twoPhaseCommitter) execute(ctx context.Context) (err error) {
//...
if commitTSMayBeCalculated && c.needLinearizability() {
latestTS, err := c.store.oracle.GetTimestamp(ctx, &oracle.Option{TxnScope: oracle.GlobalTxnScope})
//...
// Plus 1 to avoid producing the same commit TS with previously committed transactions
c.minCommitTS = latestTS + 1
}
//...
}
- TiDB发送给TiKV的prewrite请求中带上minCommitTS,它收到c.minCommitTS, c.StartTS, c.forUpdateTS影响。
func (c *twoPhaseCommitter) buildPrewriteRequest(batch batchMutations, txnSize uint64) *tikvrpc.Request {
//...
c.mu.Lock()
minCommitTS := c.minCommitTS
c.mu.Unlock()
if c.forUpdateTS > 0 && c.forUpdateTS >= minCommitTS {
minCommitTS = c.forUpdateTS + 1
} else if c.startTS >= minCommitTS {
minCommitTS = c.startTS + 1
}
//...
- TiKV端根据maxTS,请求中的minCommitTS, forUpdateTs计算出最终MinCommitTS,并保存在
lock.min_commit_ts字段中, 然后在prewriteResp.minCommitTS给TiDB client, TiDB client更新twoPhaseCommitter的minCommitTs.
func (action actionPrewrite) handleSingleBatch(c *twoPhaseCommitter, bo *Backoffer, batch batchMutations) error {
//...
if c.isAsyncCommit() {
if prewriteResp.MinCommitTs == 0 {
// fallback到normal commit
}else {
c.mu.Lock()
if prewriteResp.MinCommitTs > c.minCommitTS {
c.minCommitTS = prewriteResp.MinCommitTs
}
c.mu.Unlock()
}
TiKV端计算min commit ts
每次TiDB的prewrite请求,TiKV都会返回一个minCommitTS, minCommitTS流程如下
关键函数在async_commit_timestamps, 这个地方为什么要lock_key ?
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { // The final_min_commit_ts will be calculated if either async commit or 1PC is enabled. // It's allowed to enable 1PC without enabling async commit. fn async_commit_timestamps(/*...*/) -> Result<TimeStamp> { // This operation should not block because the latch makes sure only one thread // is operating on this key. let key_guard = CONCURRENCY_MANAGER_LOCK_DURATION_HISTOGRAM.observe_closure_duration(|| { ::futures_executor::block_on(txn.concurrency_manager.lock_key(key)) }); let final_min_commit_ts = key_guard.with_lock(|l| { let max_ts = txn.concurrency_manager.max_ts(); fail_point!("before-set-lock-in-memory"); let min_commit_ts = cmp::max(cmp::max(max_ts, start_ts), for_update_ts).next(); let min_commit_ts = cmp::max(lock.min_commit_ts, min_commit_ts); lock.min_commit_ts = min_commit_ts; *l = Some(lock.clone()); Ok(min_commit_ts) } ... } }
TiKV MaxTS
TiDB 的每一次快照读都会更新 TiKV 上的 Max TS。Prewrite 时,Min Commit TS 会被要求至少比当前的 Max TS 大,也就是比所有先前的快照读的时间戳大,所以可以取 Max TS + 1 作为 Min Commit TS
每次读操作,都会更新concurrency_manager.max_ts
值得注意的是replica read 也会更新max_ts。replica reader 在read之前会发readIndex消息给leader
因果一致性
循序性要求逻辑上发生的顺序不能违反物理上的先后顺序。具体地说,有两个事务 T1 和 T2,如果在 T1 提交后,T2 才开始提交,那么逻辑上 T1 的提交就应该发生在 T2 之前,也就是说 T1 的 Commit TS 应该小于 T2 的 Commit TS。 3
为了保证这个特性,TiDB 会在 prewrite 之前向 PD TSO 获取一个时间戳作为 Min Commit TS 的最小约束。由于前面实时性的保证,T2 在 prewrite 前获取的这个时间戳必定大于等于 T1 的 Commit TS,而这个时间戳也不会用于更新 Max TS,所以也不可能发生等于的情况。综上我们可以保证 T2 的 Commit TS 大于 T1 的 Commit TS,即满足了循序性的要求。